Best Describe Spontaneous and Phasic Flow in a Vein
With increased blood pooling in the legs comes heavier legs swelling pain from swelling pitting in the skin leakage of fluid and blood into the tissues leakage of the fluid onto the skin. Vian and axillary veins.

The Importance Of Monophasic Doppler Waveforms In The Common Femoral Vein Lin 2007 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
Non-spontaneous flow lack of pulsatility lack of phasic flow.

. Normal lower extremity venous sonography demonstrates spontaneous and phasic flow whereas upper extremity venous flow dynamics are pulsatile due to the proximity of the heart. Supine with legs externally rotated D. In duplex ultrasonography blood flow in normal vein is spontaneous phasic with respiration and can be augmented by manual pressure.
Some describe scanning the superficial venous system like scanning a plate of spaghetti. All of the following describe normal portal venous flow except. Phasic venous flow variation with respiration is surrounded by controversy and not well understood.
Sitting with legs dangling. What is the significance of that finding. 1 to act as conduit vessels transporting blood back to the heart from the bodys organs and tissues ie the venous return.
There was preserved spontaneous venous phasic flow in the RIJV around the mass and the vein was otherwise compressible with no other findings to suggest a deep vein thrombosis. And 2 to act as capacitance vessels accommodating large volumes of bloodAt rest the venous structures contain approximately two-thirds of the total blood volume. Thick skin allows for adequate penetration of infrared light.
Describe abnormal hepatic vein doppler interpretation. Your venous duplex study documents spontaneous phasic flow in the femoral vein which is displayed below the baseline. Spontaneous phasic flow C.
The patient had no prior history of right neck surgery or. Spontaneous pulsatile flow Patient positioning for a venous PPG refill study should be. There are three types of venous ultrasonography.
Posterior tibia vein flow is too slow A normal venous signal is described as being. VENOUS FLOW SPONTANEOUS PHASIC FLOW Venous flow responds to respiration. Requires little assistance from the patient.
Spontaneous pulsatile flow D. Veins as capacitance vessels. There are two principal functions of veins.
Absence of flow C. Collateral flow pattern d. An advantage of venous plethysmography is.
The best patient position for duplex imaging for lower extremity deep vein thrombosis is. In a typical adult heart baselineresting left coronary blood flow typically ranges between 05 and 10 mLming 270 331 918 919. When the phasic pattern is absent flow is defined as continuous indicating the presence of venous outflow obstruction.
A superficial vein exposed to external force can sustain endothelial damage with resulting edema and leukocyte activation that predisposes to thrombosis. The best diagnosis is an echinococcal cyst. For iliac vein obstruction phasic flow measured in the common femoral vein usually disappears and a spontaneous low velocity flux can be observed Figure 11.
Venous flow dynamics differ in the upper and lower extremities. In a transverse veiw which renal artery sits more anterior. 11 An analysis of the collateral veins is useful.
Before the development of sonography the clinical diagnosis of lower extremity thrombus was confirmed by venography using invasive injection of contrast material into the lower leg vein. Which of the following terms best describes a normal venous signal in the lower extremity. Which of the following best describes the effects of exercise on blood flow in a non-diseased vessel.
Obstruction is determined by direct planimetric measurements of the luminal diameters flow velocity changes peak vein velocity ratio of 25 low. Spontaneous non-phasic flow B. A means to measure volume increase in the lower extremities.
Revzin Hjalti Thorisson Ulrike M. Compression ultrasound B-mode imaging only duplex ultrasound B-mode imaging and Doppler waveform analysis and color Doppler imaging alone. B The portal venous system demonstrates.
When performing venous sonography of a unilateral upper extremity examination. This is due to incompetent valves in the veins. What type of flow is normally found in the SMA and IMA post prandial.
Vein is compressible C. This signifies venous reflux. Celiac SMA and IMA.
8 Prominent varicose veins are both more likely to have decreased flow rates and venous stasis as well as local external injury contributing to the higher incidence of SVT. As you manually compress the external ilian vein just above the inguinal ligament flow is above the baseline. Greater Lessor Small Perforators.
Deep and superficial veins of the lower extremity. Phasic blood flow C. Deep venous thrombosis DVT of the lower extremity veins is a common entity with important clinical consequences if untreated.
The development of extensive iliofemoral thrombosis occurring and producing a clinical pattern of tight leg edema sever pain and cyanotic mottled skin. Counterintuitively the phasic nature of left ventricular blood flow does not result in lower absolute flow values when compared to the right side of the heart. Blood flow in normal veins is spontaneous and phasic with respiration and can be augmented by manual compression distal to the ultrasound transducer.
Superficial veins flow to the major superficial veins - Saphenous Veins. As lower-limb veins are often duplicated or triplicated and connected with numerous collateral veins a collateral pathway develops when. The current concept assigns a major role to the abdominal pump According to this model inspiratory increases in abdominal pressure compress the vena cava increasing its internal venous pressure and propelling blood upstream.
The following are spectral and color Doppler characteristics of normal veins except aphasic flow in large veins bspontaneous flow in large and medium veins. Supine with head elevated B. An abscess is a possibility although with a history of being a sheep herder echinococcal cyst is more likely.
Ultrasound Evaluation of the Portal and Hepatic Veins Leslie M. In Western countries PHT most commonly occurs secondary to underlying liver cirrhosis either viral or alcohol induced. It is very good at detecting the location of thrombus.
The issue is one of vein hypertension due to the impeded flow of blood returning to the heart especially in the legs. PARAMETERS OF NORMAL VENOUS FLOW Venous flow. Continuous venous flow B.
What three vessels are involved with bowel ischemia. Hamper Portal hypertension PHT is an extremely common medical problem worldwide. Morbidity is primarily related to.

Doppler Interrogation Of The Femoral Vein In The Critically Ill Patient The Fastest Potential Acoustic Window To Diagnose Right Ventricular Dysfunction Abstract Europe Pmc
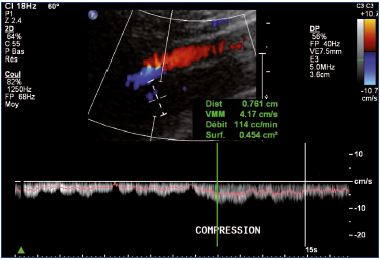
Role Of Duplex Ultrasound Investigation In The Management Of Postthrombotic Syndrome Servier Phlebolymphologyservier Phlebolymphology

Spontaneous And Phasic Venous Flow Waveform On Ultrasound Google Search Ultrasound Medical Ultrasound Diagnostic Medical Sonography

Spectral Doppler Waveform Analysis Of The Lower Limb Veins Spontaneous Download Scientific Diagram

Spectral Doppler Waveform Analysis Of The External Iliac Vein Eiv Download Scientific Diagram
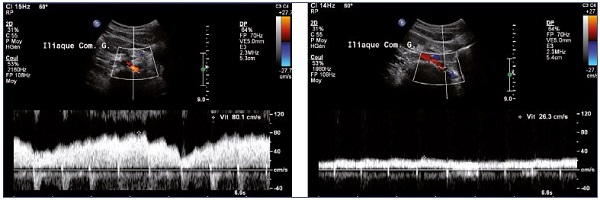
Role Of Duplex Ultrasound Investigation In The Management Of Postthrombotic Syndrome Servier Phlebolymphologyservier Phlebolymphology

Doppler Ultrasound Of Normal Venous Flow

An Example Of Normal Respiratory Phasicity Of Venous Fl Ow As The Download Scientific Diagram
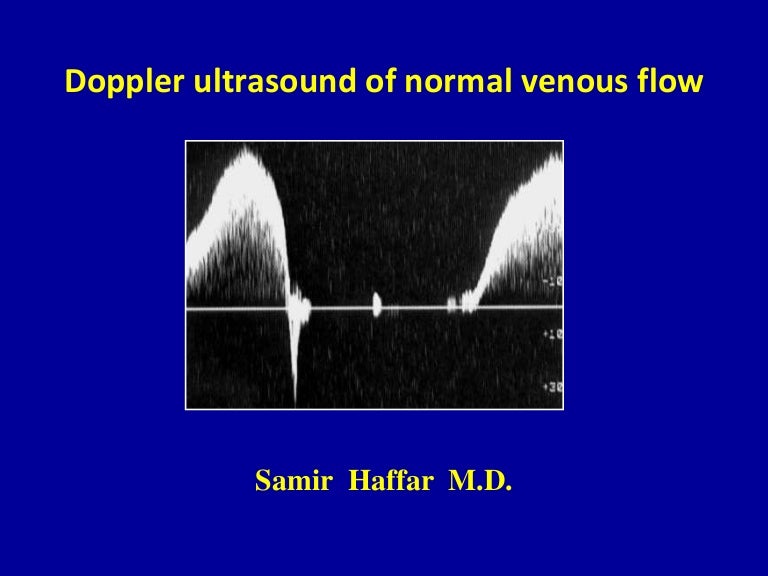
Doppler Ultrasound Of Normal Venous Flow

Triplex Of A Cephalic Vein With A Flow Measurement Arrow Download Scientific Diagram

Venous Doppler Sonography Of The Extremities A Window To Pathology Of The Thorax Abdomen And Pelvis Semantic Scholar

Colour Flow Doppler And Pulsed Doppler Spectral Waveform At The Right Download Scientific Diagram

Doppler Ultrasound Of Normal Venous Flow

Mechanical Function Of Internal Jugular Vein Valve Post Analysis Of M Mode Imaging Under Cardiac Monitoring Ultrasound In Medicine And Biology

Side Difference Of The Venous Flow In The Distal Subclavian Vein In A Download Scientific Diagram



Comments
Post a Comment